Blood Overview
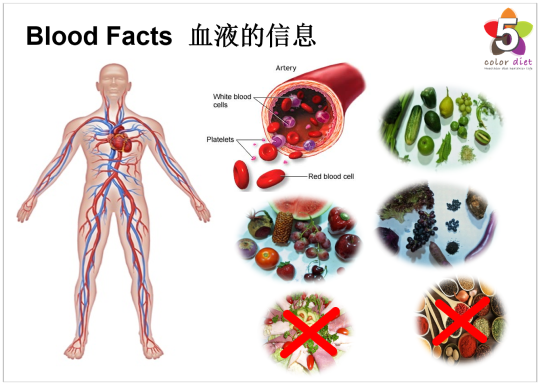
Approximately 8% of an adult’s body weight is made up of blood. Females have around 4-5 litres, while males have around 5-6 litres. It has a pH of 7.35-7.45, making it slightly basic (less than 7 is considered acidic). Whole blood is about 4.5-5.5 times as viscous as water, indicating that it is more resistant to flow than water. This viscosity is vital to the function of blood because if blood flows too easily or with too much resistance, it can strain the heart and lead to severe cardiovascular problems. Blood in the arteries is a brighter red than blood in the veins because of the higher levels of oxygen found in the arteries.
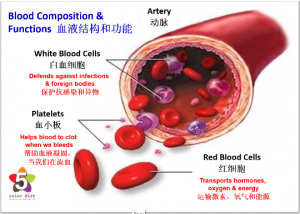
In Western Medicine, blood is composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, nutrients, other proteins, electrolytes and water. Its main functions are distributing hormones, carrying oxygen and energy (glucose) and supporting the immune system. Its white blood cells have antibodies which defend us from infections and foreign bodies, while platelets help the blood to clot (coagulate) when we are bleeding. It also regulates our acidity (pH) levels & our body temperature.
Risk Factors For Blood Diseases/ Cancer
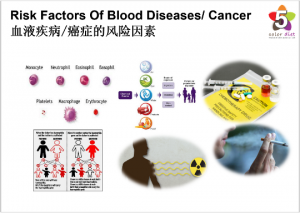
The causes of blood cancer are still unclear, however, there are certain risk factors that are associated with blood cancer. The causes of blood cancer can be genetic.
● Certain Blood Disorders: Blood disorders seems to be increasing the risk of blood cancer. These disorders include chronic Myeloproliferative (condition that causes the blood cells to grow rapid and abnormally), polycythemia Vera (body starts generating too many red blood cells), essential thrombocythemia (body produce too many blood platelets), and idiopathic myelofibrosis (bone marrow disorder, where the bone marrow starts disrupting production of blood cells and replace them with fiber scar-like substances). The risk increases if the treatment of these disorders includes chemotherapy.
● Chemicals Exposure: Certain chemicals, including some used in chemotherapy treatments used for cancer, can increase a person’s risk of developing blood cancer. One chemical in particular that can increase the risk of certain blood cancers is benzene. Benzene can be found in cigarette smoke, many cleaning products, detergents, art supplies, paint strippers, and glue. Benzene can also be used in the rubber, chemical, oil, and gasoline industries.
● Chemotherapy Drugs: The patients who have been treated with chemotherapy, have high risk of developing blood cancer.
● Gender: Some blood cancers occur more often in males than females. However, this does not mean that females do not get blood cancer. There are simply a higher percentage of males who get certain blood cancers than females.
● Genetic: Having a close family member (like a parent or a sibling) who has a certain blood cancer can potentially increase a person’s risk of developing the disease.
(1) Some syndromes that cause blood cancer are genetic, like Fanconi anemia (a genetic defect), Bloom syndrome (genetic disorder), Ataxia-telangiectasia (a genetically inherited disease causing several disabilities), Diamond-Blackfan anemia (inherited pure red cell aplasia), Schwachman-Diamond syndrome (congenital disorder), Li-Fraumeni syndrome (cancer predisposition hereditary disorder), Neurofibromatosis type 1 (tumor disorder caused by mutation), Severe congenital neutropenia (also called Kostmann syndrome), etc.
(2) Some problems those are present at birth:
● Born with an extra copy of chromosome 21.
● Born with an extra copy of chromosome 8.
● Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to radiation treatment for other cancers can increase the risk of developing blood cancer. The effect of radiation was studied in people exposed to the atomic bombs in Japan. Generally, the higher the dose of radiation, the greater the risk of developing blood cancer, and the extreme doses of radiation at the atomic bomb sites, as well as at nuclear reactor accident sites, greatly increases the risk of blood cancer. Radiation exposure can occur in a workplace, as a result of previous cancer treatment, or as a result of imaging tests, like computed tomography (CT) scans or x-rays, although the risk can vary greatly between these different types of exposure.
● Smoking: This is the only confirmed lifestyle related risk factor for blood cancer. Smoking is commonly known for causing lung cancer or mouth cancer, however, it also affect the cells that indirectly come in contact with smoke, like blood cells.
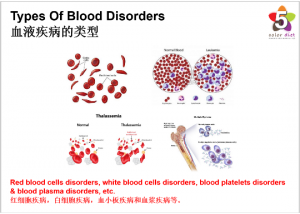
Types of Blood Disorders
Blood disorders can affect any of the three main components of blood:
● Red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the body’s tissues.
● White blood, which fight infections.
● Platelets, which help blood to clot.
Blood disorders can also affect the liquid portion of blood, called blood plasma. Treatments and prognosis for blood diseases vary, depending on the blood condition and its severity.
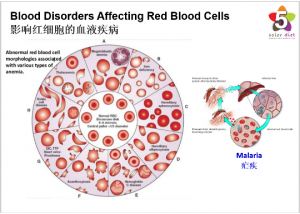
Blood Disorders Affecting Red Blood Cells
Blood disorders that affect red blood cells include:
● Anemia: People with anemia have a low number of red blood cells. Mild anemia often causes no symptoms. More severe anemia can cause fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath with exertion.
● Anemia Of Chronic Diseases: People with chronic kidney disease or other chronic diseases tend to develop anemia. Anemia of chronic disease does not usually require treatment. Injections of a synthetic hormone, epoetin alfa (Epogen or Procrit), to stimulate the production of blood cells or blood transfusions may be necessary in some people with this form of anemia.
● Aplastic Anemia: In people with aplastic anemia, the bone marrow does not produce enough blood cells, including red blood cells. This can be caused by certain health conditions, including hepatitis, Epstein-Barr, or Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) to the side effect of a drug, to chemotherapy medications, to pregnancy. Medications, blood transfusions, and even a bone marrow transplant may be required to treat aplastic anemia.
● Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: In people with this condition, an overactive immune system destroys the body’s own red blood cells, causing anemia. Medicines that suppress the immune system, such as prednisone, may be required to stop the process.
● Iron-Deficiency Anemia: Iron is necessary for the body to make red blood cells. Low iron intake and loss of blood due to menstruation are the most common causes of iron-deficiency anemia. It may also be caused by blood loss from the Gastrointestinal tract because of ulcers or cancer. Treatment includes iron pills, or rarely, blood transfusion.
● Pernicious Anemia (Vitamin B12 deficiency): A condition that prevents the body from absorbing enough Vitamin B12 in the diet. This can be caused by a weakened stomach lining or an autoimmune condition. Besides anemia, nerve damage (neuropathy) can eventually result.
● Sickle Cell Anemia: A genetic condition that affects mostly people whose families have come from Africa, South or Central America, the Caribbean islands, India, Saudi Arabia, and Mediterranean countries that include Turkey, Greece, and Italy. In sickle cell anemia, the red blood cells are sticky and stiff. They can block blood flow. Severe pain and organ damage can occur.
● Thalassemia: This is a genetic form of anemia that mostly affects people of Mediterranean heritage. Most people have no symptoms and require no treatment. Others may need regular blood transfusions to relieve anemia symptoms.
● Malaria: A mosquito’s bite transmits a parasite into a person’s blood, where it infects red blood cells. Periodically, the red blood cells rupture, causing fever, chills, and organ damage. This blood infection is most common in parts of Africa but can also be found in other tropical and subtropical areas around the world. Those traveling to affected areas should take preventive measures.
● Polycythemia Vera: The body produces too many blood cells, from an unknown cause. The excess red blood cells usually create no problems but may cause blood clots in some people.
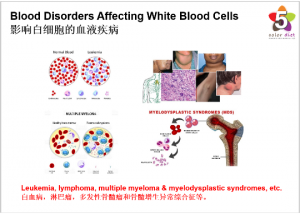
Blood Disorders Affecting White Blood Cells
Blood disorders that affect white blood cells include:
● Leukemia: A form of blood cancer in which a white blood cell becomes malignant and multiplies inside bone marrow. Leukemia may be acute (rapid and severe) or chronic (slowly progressing). Chemotherapy or stem cell transplantation (bone marrow transplant) can be used to treat leukemia, and may result in a cure.
● Lymphoma: A form of blood cancer that develops in the lymph system. In lymphoma, a white blood cell becomes malignant, multiplying and spreading abnormally. Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma are the two major groups of lymphoma. Treatment with chemotherapy or radiation can often extend life with lymphoma.
● Multiple Myeloma: A blood cancer in which a white blood cell called a plasma cell becomes malignant. The plasma cells multiply and release damaging substances that eventually cause organ damage. Multiple myeloma has no cure, but stem cell transplant or chemotherapy can allow many people to live for years with the condition.
● Myelodysplastic Syndrome: A family of blood cancers that affect the bone marrow. Myelodysplastic syndrome often progresses very slowly, but may suddenly transform into a severe leukemia. Treatments may include blood transfusions, chemotherapy and stem cell transplant.
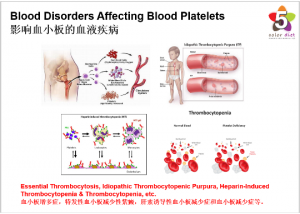
Blood Disorders Affecting Platelets
Blood disorders that affect the platelets include:
● Essential Thrombocytosis (Primary Thrombocythemia): The body produces too many platelets, due to an unknown cause; the platelets do not work properly, resulting in excessive clotting, bleeding, or both.
● Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A condition causing a persistently low number of platelets in the blood, due to an unknown cause; usually, there are no symptoms, yet abnormal bruising, small red spots on the skin (petechiae), or abnormal bleeding can result.
● Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia: A low platelet count caused by a reaction against heparin, a blood thinner given to many hospitalized people to prevent blood clots
● Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: A rare blood disorder causing small blood clots to form in blood vessels throughout the body; platelets are used up in the process, causing a low platelet count.
● Thrombocytopenia: A low number of platelets in the blood; numerous conditions cause thrombocytopenia, but most do not result in abnormal bleeding.
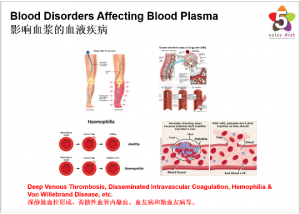
Blood Disorders Affecting Blood Plasma
Blood disorders that affect blood plasma include:
● Deep Venous Thrombosis: A blood clot in a deep vein, usually in the leg; a deep venous thrombosis can dislodge and travel through the heart to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
● Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC): A condition that causes tiny blood clots and areas of bleeding throughout the body simultaneously; severe infections, surgery, or complications of pregnancy are conditions that can lead to Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC).
● Hemophilia: A genetic deficiency of certain proteins that help blood to clot; there are multiple forms of hemophilia, ranging in severity from mild to life-threatening.
● Hypercoaguable State (hypercoagulable state): A tendency for the blood to clot too easily; most affected people have only a mild excess tendency to clot, and may never be diagnosed. Some people develop repeated episodes of blood clotting throughout life, requiring them to take a daily blood thinning medicine.
● Von Willebrand Disease: Von Willebrand factor is a protein in blood that helps blood to clot. In Von Willebrand disease, the body either produces too little of the protein, or produces a protein that does not work well. The condition is inherited, but most people with Von Willebrand disease have no symptoms and don’t know they have it. Some people with Von Willebrand disease will have excessive bleeding after an injury or during surgery.
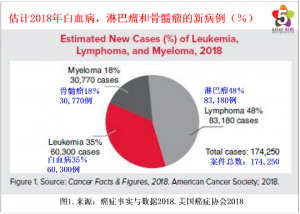
Statistics of United States in 2018 On Leukemia, Lymphoma & Myeloma
New cases of leukemia, lymphoma and myeloma are expected to account for 10 percent of the estimated 1,735,350 new cancer cases diagnosed in the US in 2018.
-
Chinese Medicine On Blood Facts
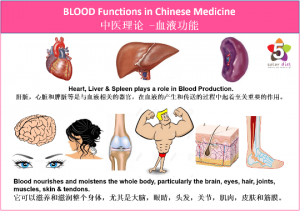
According to Chinese Medicine’s theory, blood is a fundamental substance in the body. Blood nourishes and moistens the whole body, particularly the brain, eyes, hair, joints, muscles, skin & tendons. Many aging issues are due to Blood Deficiency such as hair loss because hair growth is dependent on the quality and abundance nourishing Blood. The Liver, Heart and Spleen organs systems are the most relevant systems related to Blood which play a role in Blood production and distribution. Blood is a Yin substance.
Detoxification through taking the right food sources & herbs is one way to help eliminate toxic substances from our Bloodstream naturally & improve Blood’s health. The detoxification systems of our body need to be in priority order because each organ need to cleanse its toxins or the toxins will spread to other organs. Advisable to follow the detoxification system’s in priority order…
In Chinese medicine, Blood imbalances are associated with a variety of causes:
(1) Blood Deficiency
(2) Blood Stagnation
(3) Blood Heat
-
Dietary Recommendations For Blood Deficiency
Blood Deficiency is not a disease but a health problem that can be improved with right food therapies & remedies. Once, long term Blood Deficiency develops in the body, it takes at least 6-8 months to rectify its symptoms with right food therapies & remedies.
Pattern Description Causes Of Blood Deficiency ● Caused by Blood Stagnation. ● Caused by general Blood Deficiency include blood loss due to trauma, surgery or a diminished blood production.
● Caused by Spleen Qi deficiency (Spleen provides raw materials). When Blood becomes deficient, the Heart and Liver are especially affected. (Heart governs Blood while Liver stores Blood).
● Chronic nutritional deficiencies, etc.
● Gynaecology problems (eg: heavy, scant or irregular menses & fibroids or polycystic ovary syndrome).
Symptoms Of Blood Deficiency Anemia, anxiety, blurred vision, brittle & pale nails, chronic fatigue syndrome, cracking joints, difficulty falling asleep, dry eyes, skin & hair, depression, dizziness, fatigue, gynaecology problems (eg: heavy, scant or irregular menses), hair loss or premature greying, headache (especially around eyes), heart palpitations, insomnia, irregular heartbeat, itchy or easy bruising skin, low back pain, low energy, migraines, muscles cramps & spasms, nervousness, numbness or tremors of hands & feet, pale face & lips, poor digestion functions, poor memory & vertigo, etc. Tongue: pale on both sides.
Related Health Problems Of Blood Deficiency Anemia, malnutrition, menstrual disorders & neurasthenia, etc. Recommended Food Sources For Improving Body Imbalance Related To Blood Deficiency ● Beans: Almonds, black sesame seeds, black soybeans, cashew nuts, chick peas, Chinese almonds, fava beans, kidney beans, red beans, sesame seeds, sunflower seeds, miso paste & tempeh, etc. ● Fruits: Apple, apricot, avocado, berries, cherries, coconut, dates, figs, goji berries, grapes, longan, lychee, mulberries, stewed fruits and especially dark green/ orange/ yellow/ red/ black/ purple & blue fruits, etc.
● Grains: Cooked whole grains, amaranth, roasted barley, brown rice, buckwheat, Chinese barley, glutinous rice, millet, oats, quinoa & wheat bran, etc.
● Herbs & Spices: Dang Shen, dong quai, garlic, ginseng, ginger, Korean ginseng, onions, parsley, turmeric & wheatgrass, etc.
● Meat & Seafood: Animal livers & kidneys, chicken, mussels, octopus, oysters, red meat, deep-sea fish (Eg: salmon & tuna), etc.
● Vegetables: Alfalfa sprouts, artichoke, beetroot, button mushrooms, carrot, corn, dandelion leaf, green peas, kale, leeks, parsnips, pumpkin, shiitake mushrooms, spinach, sweet potatoes, wheatgrass, taro root, yams and especially dark green/ orange/ yellow/ red/ black/ purple & blue vegetables, etc.
● Others: Blackstrap molasses, marmite and Teas (Eg: Dang Shen, Dong Quai, ginger, ginseng, turmeric, lavender flowers & rosebuds), etc.
● Food diet should comprise of Proteins 20-30%, Complex carbohydrates 20-30% like grains and starchy root vegetables & Cooked vegetables 30-40%.
Foods To Avoid Or Least Intake For Improving Body Imbalance Related To Blood Deficiency ● Alcohol, caffeine beverages, carbonated beverages, chocolates, cold raw foods (Eg: iced drinks, raw meat, salads or white/ tan & brown fruits & vegetables), dairy products (Eg: butter, cheese, eggs & milk except yogurt), fried or greasy foods, processed foods & refined sugars (Eg: biscuits, cakes & pastries), etc. ● Excessive of Vitamin C (Not more than 3,000 mg).
● Avoid smoking & stress.
-
Dietary Recommendations For Blood Stagnation
Blood Stasis Syndrome or Stagnation is where the normal flow of Blood has become obstructed. Stagnant Blood can occur in the channels (usually due to trauma), or in the internal organs, mainly in the Liver, Heart, Uterus, Intestines & Stomach. Heat in the Blood also eventually causes blood to stagnate & affect body internal coldness.
Pattern Description Causes Of Blood Stagnation ● Abortions or heavy blood loss during childbirth. ● Caused by long term Qi & Blood Deficiencies, or excesses of heat or cold in the body.
● Intake of too much cold foods like iced drinks, salads or white/ tan and brown fruits & vegetables.
● Intra-abdominal surgery, traumatic injury or surgery.
● Intercourse during menstruation.
● In women, advisable not to take cold foods or drinks 1 week before menstruation or during menstruation period.
Symptoms Of Blood Stagnation Anxiety, bruising on skin or varicose veins, chronic inflammation of the abdomen, chest & pelvis, clot & dark menstrual blood, dark skin that lacks luster, depression, fatigue, feel uncomfortable in cold environments, headaches, insomnia, menstrual disorders, poor blood circulation, sharp stabbing or cutting pain in the head, eyes, joints or other internal organs, sluggish bowel movements, stiff neck & shoulders, sweat easily, swellings or masses such as non-malignant tumors, cysts and fibroids, vivid dreams, etc. Tongue: purple color possibly with purple spots, red purple color if there is heatiness in the body or blue purple if there is coldness in the body. Related Health Problems Of Blood Stagnation Bleedings, breast distension or lumps, chest pain, chronic fatigue syndrome, depression, endometriosis, enlarged liver or spleen, hemoptysis (coughing up blood), hypochondriac (meaning below the ribs) pain, insomnia, irritable bowel syndrome, migraine headaches, menstrual disorders, palpable masses in the abdomen, polycystic ovaries, poor circulation, subcutaneous hematoma (bruising under the skin), thyroid problems, uterine fibroids, growth & tumours in some organs, etc. Recommended Food Sources For Improving Body Imbalance Related To Blood Stagnation ● Beans, Nuts & Seeds: Almonds, black beans, chestnuts, Chia seeds, Chinese almonds, flaxseeds, gingko nuts, kidney beans, pine nuts, pumpkin seeds, red beans, walnuts, soybeans, miso paste & tempeh, etc. ● Fruits: Apricot, banana, citrus fruits, hawthorn fruit, lemon, mango, papaya, peach, plum, raisins, sour jujube, sugar cane, especially most green/ orange & yellow color fruits, etc.
● Grains: Amaranth, cereals, oats, quinoa & white rice, etc.
● Herbs & Spices: Alfalfa, basil, Burdock, chives, Dang Shen, garlic, ginger, licorice, lotus leaf, onions, nutmeg, parsley, rosemary, sage, shallots, turmeric & white pepper, etc.
● Meat & Seafood: Abalone, clams, crab, fish, jellyfish, lean meat & sea cucumber, etc.
● Vegetables: Asparagus, black fungus, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, carrot, celery, Chinese radish, eggplants, kelp, leeks, mushrooms, pumpkin, seaweed, spinach, taro root, yams, zucchini especially most green/ orange & yellow color vegetables, etc.
● Others: Brown sugar, healthy oils (eg: canola oil, olive oil, safflower oil), vinegar and Teas (Eg: chrysanthemum, green tea, lavender flowers & rosebuds), etc.
● Food diet should comprise of Proteins only 10%, Complex carbohydrates 30% like grains and starchy root vegetables & Cooked vegetables 40-60%.
Foods To Avoid Or Least Intake For Improving Body Imbalance Related To Blood Stagnation ● Alcohol, all nuts & seeds except those stated in Recommended food sources, caffeine beverages, carbonated beverages, chocolate, cold raw foods (Eg: iced drinks, salads or white/ tan & brown fruits & vegetables), dairy products (Eg: butter, cheese, eggs & milk except yogurt), fried or greasy foods, grains (Eg: brown rice & millet), processed foods, refined sugars (Eg: biscuits, cakes & pastries), red meat, salt, spicy foods & tomatoes, etc. ● Excessive of Vitamin C (Not more than 3,000 mg).
● Avoid smoking & stress.
-
Dietary Recommendations For Blood Heat
In Traditional Chinese Medicine, blood is viewed simply as the red fluid circulating within the vessels, it relies on the regulations of internal organs to distribute efficiently throughout the body. Blood is transformed by the spleen; stored by the liver; pushed by the heart; disseminated by the lungs; and transformed into life essence by the kidneys.
Excessive heat will damage the blood vessels and results in “reckless” movement of hot blood. Bleeding can occur from Blood Heat in conditions such as nosebleed, vomiting up blood, heavy periods, bleeding between periods, blood in the urine or stools, bleeding gums. The hotter the Blood Heat, the redder the blood lost, the faster it flows and the more profusely. However, bleeding can be due to other syndromes in Chinese Medicine, such as Blood Stasis, Qi deficiency and even Yin deficiency, but in these conditions the Blood is less urgent and, except for Qi deficiency when bleeding can go on heavily for some time, usually less in quantity. If the stools are blacker than usual, this may be from blood-loss further up the intestines. This might be from an intestinal ulcer or from cancer. You should seek medical attention immediately.
Pattern Description Causes Of Blood Heat ● In Chinese Medicine, the Heart may not be controlling the Blood, and the Spleen not keeping it in place. ● Chronic diseases & medications.
● Emotional disorders.
● Excessive alcoholic drinks.
● Excessive greasy, fried, spicy foods & drinks.
● Long exposure to hot conditions, including radiators, the sun and fire, etc.
Symptoms Of Blood Heat Bleeding gums, bleeding between periods, blood in the urine or stools, haemorrhoids, nosebleeds, sore throat, toothache, ulcerative colitis, vomiting up blood, skin problems (Eg: acne, boils, dermatitis, eczema, red rashes & itching), etc. Tongue: Red color with ulcers in the mouth or tongue.
Related Health Problems Of Blood Heat Bleedings in gums, nose, tongue or under the skin, blood in semen, stools, urine or vomiting blood, gynaecological disorders & skin problems, etc. Recommended Food Sources For Improving Body Imbalance Related To Blood Heat ● Beans, Nuts & Seeds: Adzuki beans, almonds, beancurd, bean sprouts, Chinese almonds, green beans, hyacinth beans, lotus seeds, soybeans, miso paste & tempeh, etc. ● Fruits: Banana, cranberries, lemon, loquat, persimmons, watermelon, especially most green/ orange & yellow color fruits, etc.
● Grains: Amaranth, barley, Chinese barley, millet, rice, rye & whole wheat, etc.
● Herbs & Spices: Mulberry leaves & peppermint leaves.
● Meat & Seafood: duck & all fishes.
● Vegetables: Alfalfa sprouts, amaranth leaves, arugula, asparagus, bamboo shoots, bittergourd, bok choy, broccoli, cabbage, cauliflower, carrots, Chinese cabbage, celery, cucumber, eggplants, kelp, lettuce, lotus root, mushrooms, peas, purslane, radish, spinach, Swiss chard, tomatoes, water chestnuts, watercress, wax gourd, wild rice stems, zucchini especially most green/ orange & yellow color vegetables, etc.
● Others: Coconut oil, flaxseed oil, olive oil and Teas (Eg: Chinese barley, chrysanthemum, chrysanthemum leaves, green tea, mulberry leaves & peppermint leaves), etc.
● Food diet should comprise of Proteins only 20%, Complex carbohydrates 20-30% like grains and starchy root vegetables & Cooked vegetables 50%.
Foods To Avoid Or Least Intake For Improving Body Imbalance Related To Blood Heat ● Alcohol, carbonated beverages, caffeine beverages, cold & raw foods (Eg: iced drinks, raw meat, salads or white/ tan & brown fruits & vegetables), dairy products (Eg: butter, cheese, eggs & milk except yogurt), fried or greasy foods, processed foods, pungent herbs (Eg: basil, capsicum, chili, cinnamon, cloves, garlic, ginger, horseradish, leeks, onions, shallots, turmeric), red meat, refined sugars (Eg: biscuits, cakes & pastries), salt, shrimps, spicy foods, etc. ● Excessive of Vitamin C (Not more than 3,000 mg).
● Do not take too much medications.
● Avoid smoking & stress.
-
Supplementary For Improving Blood Problems
● Herbs: Arnica, Artichoke, Beetroot, Burdock, Chlorella, Dandelion, Dang Sheng, Dong Quai, Ginseng, Licorice, Milk Thistle, Nettle, Royal Jelly, Schisandra, Skullcap, Spirulina, Turmeric, Wheatgrass & White Willow Bark, etc.
● Amino Acids, Vitamins & Minerals: Alpha Lipoic Acid, Carnitine, Lysine, Methionine, Vitamin A, Vitamin B12, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, Folic Acid, Iron, Nickel, Selenium, Zinc & fiber.
Note:
(1) To take supplements at an interval of 1 to 2 hours from caffeine beverages or medication.
(2) Consult health experts’ advice shall you need to take any supplements, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding or having any medical conditions.
-
Alternative Therapies For Improving Blood Problems
● Apply footbath for Blood’s detox. Use natural ingredients like herbs & vegetables per above Recommended Food Sources For Blood’s Body Imbalances related to each pattern.
● Exercise minimum 30 minutes at 3 to 5 times weekly will help to promote blood circulation & metabolism which will contribute to a healthy immune system.
● Apply meditation 1 to 2 times daily to calm the nerves, emotional mood imbalances & reduce stress.