Overview
Some researches showed that over 25% of people don’t get enough sleep from time to time, but almost 10% have chronic insomnia. Insomnia is not a disease; rather, it is a complex symptom. Insomnia can be acute, meaning short-term. Or it can come in a long-lasting, chronic form. When insomnia comes at least 3 nights a week for 3 months or longer, doctors consider it chronic. Insomnia can also come and go, with periods when you have no sleep problems.
There are 2 types of Insomnia. (1) Primary insomnia: Sleep problems are not directly connected with any other health problem. Instead, they are triggered by major stress, emotional upset, travel, and work schedules. But even after such causes go away, the insomnia may persist. You can also develop primary insomnia because of certain habits, such as taking naps or worrying about sleep.
(2) Secondary insomnia: Sleep problems occur because of another issue, such as a sleep disorder like apnea; another health condition or disease; chronic pain from arthritis or headaches; medications; or alcohol, caffeine, and other substances.
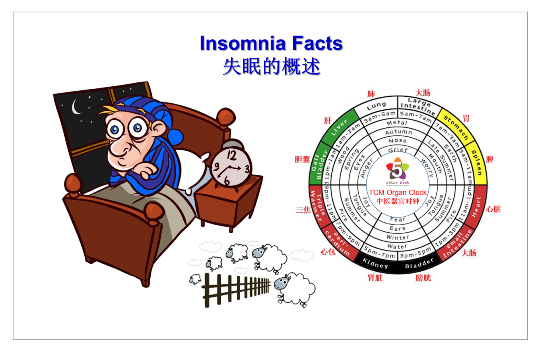
In Chinese medicine’s theory, insomnia is related to low or excess energy of body organs of heart, spleen, liver & kidneys. It stresses the need to observe the body’s natural daily cycle. The “organ time clock” specifies certain times for restoring the energy of certain organs:
- Gallbladder: 23:00 pm to 01:00 am.
- Liver: 01:00 am to 03:00 am.
- Lungs: 03:00 am to 05:00 am.
- Large Intestine: 05:00 am to 07:00 am.
It helps to go to bed early for optimum benefits. 21.00 pm sleep time is the most preferable.
-
Causes Of Insomnia
● Age: Insomnia increases with age as our sleep patterns change. Older adults often have trouble with sustained sleep over an eight-hour period. They may need to nap during the day to get the recommended eight hours of sleep over a 24-hour period. According to the Mayo Clinic, some estimates suggest that nearly half of all men and women over 60 years old experience symptoms of insomnia.
● Alcohol: People commonly use alcohol as a sleep aid. However, alcohol often interferes with sleep later in the night. When used on a regular basis over the long-term, you can become dependent on alcohol and develop severe insomnia if you stop drinking alcohol. Due to numerous health risks, alcohol is not recommended at bedtime for people with insomnia.
● Caffeine beverages: Coffee, tea, soft drinks & energy drinks contain caffeine that stimulates the brain. This stimulus can interfere with sleep. Drinking coffee in the late afternoon can keep you from falling asleep at night.
● Depression: Depression is a common source of insomnia. This may be due to imbalances in brain chemicals that affect sleep patterns. Alternately, you may be too distressed by fears or troubling thoughts that can come with depression to sleep well.
● Drug medications: A number of over-the-counter medications can cause insomnia. Pain medications, allergy drugs, antidepressants, decongestants, heart & blood pressure medicines and weight-loss products can contain caffeine or other stimulants. Antihistamines may make you drowsy at first, but they can lead to frequent urination that means more nighttime trips to the bathroom.
● Environmental changes: Shift work or long-distance travel can affect your body’s circadian rhythm. This is the 24-hour biochemical, physiological, and behavioral cycle affected by your exposure to sunlight. This rhythm is your internal clock. It regulates sleep cycles, body temperature & metabolism.
● Gender: Women are twice as likely to experience insomnia as men. Hormonal shifts during the menstrual cycle and in menopause are thought to be responsible for sleeplessness. Insomnia often occurs during the time leading up to menopause (perimenopause) when night sweats and hot flashes commonly disturb sleep. Experts believe a lack of estrogen may contribute to sleep difficulties in postmenopausal women.
● Health problems: Some medical conditions can contribute to insomnia, such as: Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s disease, arthritis, asthma, breathing difficulties, cancers, cardiovascular diseases, chronic pain, depression, diabetes, frequent urination, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), menopause, obesity, overactive thyroid & post-traumatic stress disorder, etc.
● Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar is a common cause of sleep-maintenance insomnia. A diet high in refined carbohydrates (breads, pasta and sugar) can lead to problems in blood sugar metabolism.
● Improper diet: Eating too much foods that are greasy, hot, spicy or heavy especially before sleep can cause indigestion or heartburn which in turn, will cause insomnia.
● Lack of Exercise: A lack of exercise can contribute to restlessness at night. Daily exercise of 30 minutes per session in the morning or late afternoon can helps to improve the quality of sleep at night.
● Nutritional deficiencies: Vitamin A, B3 (niacin), B5 (pantothenic acid), B9 (folic acid), B12 (cobalamin), C, D, E, Calcium, Copper, Iron, Magnesium & Tryptophan may cause insomnia problems.
● Sleep apnea or snoring: Sleep apnea is a breathing disorder accompanied by loud snoring and shorts periods when breathing stops which cause insomnia problems. Sleeping with a bed partner who snores also can cause sleep disruption.
● Sleep disorders: Common sleep disorders like restless leg syndrome can disturb sleep. This is a crawling sensation felt in the lower part of the legs that is relieved only with movement.
● Smoking: Nicotine in tobacco is another stimulant that can inhibit sleep.
● Stress: Worries can keep your mind active at night. Issues at work or school or with family can make you anxious. This can make it difficult or impossible for you to sleep. Traumatic events like the death of a loved one, divorce, or a job loss often cause long-lasting stress and anxiety. These conditions can lead to chronic sleeplessness.
● Overweight: According to the American Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, sleeping disorders are linked to obesity. Adults who sleep less than six hours a night have a significantly higher rate of obesity (33 percent) than those who sleep seven to eight hours a night (22 percent). This pattern was found in all ages of both men and women. -
Symptoms Of Insomnia
● Attention & concentration problems.
● Daytime sleepiness.
● Difficulty falling asleep.
● Difficulty staying asleep.
● Feeling tired and irritable.
● Frustration or worry about sleep.
● Lack of motivation.
● Making errors at work, school, or while driving.
● Mood changes.
● Tension headaches or stomach aches.
● Waking up too early. -
Recommended Food Sources For Insomnia
● Nutritional deficiencies that may impair sleep are:
(1) Vitamin A: Vitamin A plays a major role in the regulation of several brain functions including sleep and memory. Foods high in Vitamin A are animal livers & kidneys, apricots, beets, dairy products (butter, cheese, milk, yogurt), fish, fish liver oil, green/ red/ orange/ yellow fruits & vegetables & meat, etc.
(2) Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Vitamin B3 (Niacin) often promotes sleep in people who have insomnia caused by depression and increases effectiveness of tryptophan. It is reported to help people who fall asleep rapidly but keep waking up during the night. Foods high in Vitamin B3 (Niacin) are animal livers & kidneys, avocado, brewer’s yeast, cereals, dates, figs, fish, legumes, meat, nuts, poultry, prunes, wheat germ, whole grains, etc.
(3) Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid): Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) is good for relieving stress and anxiety. A deficiency of Vitamin B5 can cause sleep disturbances and fatigue. Foods high in Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) are animal livers, beans, brewer’s yeast, cereals, eggs, fish, fish roe, legumes, meat, nuts, poultry, oranges, wheat germ, whole grains, etc.
(4) Vitamin B9 (Folic acid): Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) deficiency has been linked to insomnia. Foods high in Vitamin B9 (Folic acid) are avocado, asparagus, banana, beans, beetroots, broccoli, brussels sprouts, carrot, cauliflower, celery, chili, citrus fruits, corn, dark leafy green vegetables, flaxseeds, lady finger, nuts, papaya, pumpkin, raspberries, seeds, spearmint, spinach, strawberries, tomatoes & yeast extract spread, etc.
(5) Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin): Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) is reported to help insomniacs who have problems falling asleep, as well as promoting normal sleep-awake cycles. Foods high in Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) are animal livers & kidneys, beef, brewer’s yeast, dairy foods (cheese, eggs, milk & yogurt), fish (herring, mackerel, salmon, trout & tuna), fish eggs, fish fin, lamb, meat, miso paste, seafood, sea algae, seaweed, shellfish, soybean & tempeh, etc.
(6) Vitamin C & E: Both vitamins can help to improve sleep patterns. Foods high in Vitamin C are berries, broccoli, brussels sprouts, capsicum, cauliflower, citrus fruits, dark leafy green vegetables, green peas, guava honeydew, kiwi fruit, papaya, pineapple & tomatoes, etc. Foods high in Vitamin E are found particularly in fruits & vegetables. Eg: Apricot, asparagus, avocado, basil, beets, cereal, eggs, green vegetables, broccoli, canola oil, chili, chye sim, kale, kiwi, mango, meats, nuts, olive oil, oysters, parsley, poultry, pumpkin, seeds, shellfish, spinach, tomatoes, turnip greens, vegetable oils, wheat germ oil, etc.
(7) Vitamin D: Low levels of Vitamin D can result in sleeping problems along with depression, muscle pain, weight gain, lack of energy and digestive difficulties. Foods high in Vitamin D are dairy products (butter, cheese, milk, yogurt), fish eggs, fish liver oil, oily fish (cod, herring, mackerel, salmon, tuna), etc.
(8) Calcium: Calcium, especially when contained in food, has a sedative effect on the body. A Calcium deficiency in the body causes restlessness and wakefulness. Foods high in Calcium are beancurd, dairy products (cheese, milk, yogurt), green leafy vegetables, sardines, sesame seeds & soybean, etc.
(9) Copper & Iron: Poor sleep can be caused by the lack of Copper & Iron in the diet. These minerals very strongly affect sleep patterns. Keep in mind, however, that Copper & Iron need to be in proper balance with other minerals in the body, and too much of either one can cause serious side effects. Foods high in Copper are avocado, beans, cereals, cocoa, coffee, drinking water (copper plumbing), fish, nuts, seeds, miso paste, mushrooms, nuts, oats, organ meats, seafood, seeds, tea, tempeh, wheat Bran, wheat germ, whole grains, etc. Foods high in Iron are abalone, animal livers, beans, beancurd, clams, dried apricots, dried peaches, figs, fish (haddock, mackerel, sardines & tuna, etc), green peas, green leafy vegetables, mussels, nuts, oysters, red/ black/ blue & purple fruits & vegetables, red meat, poultry, scallops, seeds, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, whole grains, etc.
(10) Magnesium: Magnesium deficiency can cause nervousness, which may prevent you from sleeping. Low levels of magnesium can lead to shallower sleep and cause you to wake more during the night. Foods high in Magnesium are almonds, apples, apricot, avocados, banana, beans, broccoli, cheese, dark chocolates, dates, figs, fish, green leafy vegetables, lady finger, legumes, lentils, nuts, potatoes, pumpkin, raisins, seeds, spinach, whole grains, yogurt, etc.
(11) Tryptophan: Tryptophan is one of the elements that make you feel sleepy after a big steak or turkey dinner. It is important because of its production of serotonin, which slows down nervous activity and induces sleep. Foods high in Tryptophan are beans, cereals, cheese, chicken, chickpeas, cocoa, eggs, fruits (banana, dates, mango), legumes, meat, milk, nuts, potato skin, seafood, sea plants, seeds, soybean, whole grains, yogurt, etc.
● For insomnia related to heart-fire issue which symptoms are insomnia, irritability, mouth dryness & redness on tongue tip: Take foods in: bittergourd, gingko nuts, gingko leaves, hawthorn, lotus leaves, lotus plumule, lotus seeds, bitter foods, mulberry leaves, etc.
● For insomnia related to kidney’s low energy issue which symptoms are anxiety, depression, drowsy, fatigue, frequent urination, incontinence, insomnia & limb coldness: Take foods in: Chinese yam, dang sheng, dong quai, gingko nuts, kudzu root, linzhi, longan, lotus root, lotus seeds, maca, royal jelly, walnuts, yam, black/ purple and blue fruits & vegetables, etc.
● For insomnia related to liver-fire issue which symptoms are bitter taste on tongue, dizziness, eye soreness, insomnia & irritability: take foods in: Cassia seeds, chamomile, chrysanthemum, green beans, lemongrass, liquorice, mulberry leaves, peppermint, tangerine peel, turmeric & green/ orange & yellow fruits & vegetables, etc.
● For insomnia related to low energy & poor blood circulation’s issues which symptoms are insomnia, irritability, limb coldness, poor appetite & mental fatigue: Take foods in: American ginseng, dang sheng, dong quai, goji berries, linzhi, longan, maca, red dates, rosebuds, sour date, red/ black/ purple & blue fruits & vegetables, etc.
● Teas: Tea blend has been known to calm the nerves, relax the mind, therefore improves insomnia problems eg: Blackberry leaves, chamomile, chrysanthemum, gingko leaves, goji berries, lavender, liquorice, longan, rosebuds, peppermint & tangerine peel, etc.
● Others: Acupuncture, acupressure or massage therapy help to promote good circulation & metabolism which will help to improve insomnia problems.
● Others: Exercise minimum 30 minutes for 3 to 5 times weekly will help to promote good circulation & metabolism which will help to improve insomnia problems.
● Others: Herbal foot baths to promote sleep: Soaking our feet in hot-warm water will improve better blood circulation, metabolism and energy to our internal organs as well as removes toxins from our body. It also helps to relieve the congested state of the brain & relaxes the mind, therefore helps to improve insomnia. Eg: American ginseng, chamomile, chrysanthemum, dang sheng, dong quai, gingko leaves, hawthorn, lavender, lemongrass, liquorice, lotus leaves, lotus plummule, peppermint, rosebuds & turmeric, etc.
● Others: Meditation daily helps to calm the nerves, emotional mood imbalances & reduce stress as well as insomnia problems.Recommendations: Try out our recipes & remedies: (1) Lavender Chrysanthemum Peppermint Tea (For Insomnia related to liver-fire). (2) Lotus Plummule Chrysanthemum Licorice Tea (For Insomnia related to heart-fire & liver-fire). (3) Foot Bath for Insomnia related to liver-fire. and (4) Foot Bath for Insomnia related to heart-fire & liver-fire.
-
Foods To Avoid Or Least Intake For Insomnia
● Alcohol: People commonly use alcohol as a sleep aid. However, alcohol often interferes with sleep later in the night. When used on a regular basis over the long-term, you can become dependent on alcohol and develop severe insomnia if you stop drinking alcohol. Due to numerous health risks, alcohol is not recommended at bedtime for people with insomnia.
● Caffeine beverages: Coffee, tea, soft drinks & energy drinks contain caffeine that stimulates the brain. This stimulus can interfere with sleep. Drinking coffee in the late afternoon can keep you from falling asleep at night.
● Improper diet: Eating too much foods that are greasy, hot, spicy or heavy especially before sleep can cause indigestion or heartburn which in turn, will cause insomnia. - Supplementary For Insomnia
-
Good sleeping habits to prevent insomnia problems
● Adjust the bedroom environment (light, noise, temperature) so that you are comfortable before you lie down.
● Avoid alcohol near bedtime.
● Avoid caffeinated beverages after lunch.
● Avoid prolonged use of phones or reading devices (“e-books”) that give off light before bed. This can make it harder to fall asleep.
● Deal with concerns or worries before bedtime. Make a list of things to work on for the next day so anxiety is reduced at night.
● Do not go to bed hungry.
● Do not force sleep.
● Do not smoke (particularly during the evening).
● Exercise regularly, preferably four or more hours before bedtime.
● Maintain a regular sleep schedule (the same bedtime and wake time every day).
● Sleep only as much as necessary to feel rested and then get out of bed.
● Apply meditation before sleep.